Archive for the ‘earth-centered spirituality’ Category
[Updated 26 July 2020]
[A Celtic Conlang |Invoke for a Tongue 1 – 2 | Druid Ritual Language 1–2–3 ]

Brigid’s Cross: Crosóg Bhríde
For the gift of speech already, I thank you.
For the gift of a Celtic tongue I will make,
let my request be also my gift to you in return:
the sound of awen in another tongue, kindred
to those you once heard from ancestors
of spirit. Wisdom in words, wrought for ready use.
May your inspiration guide heart and hand,
mind and mouth, spirit and speech.
/|\ /|\ /|\
The six living insular Celtic languages — Welsh, Breton, Cornish*, Manx*, Irish and Gaelic — have survived (*or been revived) against often harsh and long odds. I won’t go into the historical challenges that the Celtic tongues share with most minority languages. And I’m not even considering any of the extinct continental Celtic tongues like Gaulish, Galatian or Lepontic.
 Suffice it to say that not one of the six living Celtic tongues is secure enough that its advocates can relax into anything resembling the ease of speakers of a world language like English. So why not learn one of these endangered languages (or revive Galatian)? After all, with such knowledge comes the ability to experience a living Celtic culture from the inside, as well as gain access in the original languages to texts that nourish Druid practice and thought. One more speaker is one more voice against linguistic and cultural extinction. In the title and first section above I invoke Brighid/Bríd and Ogma/Oghma, to give the ancient and modern Irish forms of their names. With the experiences of many contemporary and ancient polytheists in mind, I can say with some confidence that the gods honor those who go to the trouble to learn the old languages and speak to them using even a little of the ancestral tongues.
Suffice it to say that not one of the six living Celtic tongues is secure enough that its advocates can relax into anything resembling the ease of speakers of a world language like English. So why not learn one of these endangered languages (or revive Galatian)? After all, with such knowledge comes the ability to experience a living Celtic culture from the inside, as well as gain access in the original languages to texts that nourish Druid practice and thought. One more speaker is one more voice against linguistic and cultural extinction. In the title and first section above I invoke Brighid/Bríd and Ogma/Oghma, to give the ancient and modern Irish forms of their names. With the experiences of many contemporary and ancient polytheists in mind, I can say with some confidence that the gods honor those who go to the trouble to learn the old languages and speak to them using even a little of the ancestral tongues.
Or if not one of the living Celtic tongues, then how about one of the Celtic conlangs that already exist? Arvorec, Kaledonag, Galathach and others wait in the wings, in varying states of development. They could provide a ready foundation to build on — a foundation already laid.
Why not use one of them? In part out of respect for their makers, who may not want their creations associated with Druidry. Arvorec, to focus on just one for a moment, is already part of the conlang community of Ill Bethisad, and has its own con-culture (and even con-religion — An Graveth, a cousin to Druidry). In part — a significant part for me — as a Bardic offering to the gods invoked here: gods esteem the taste of human sweat. Salt flavors the sacrifice. And for the very human reason that when we invest time and energy in something, we often value it more, and can draw on dedication, creative momentum, pride, inspiration, desire and love to see it through. If a Celtic language is not my mother tongue, then let it be a foster-mother. Let this tongue be one I have helped craft from the shapes and sounds and world we receive as a heritage.
/|\ /|\ /|\
Like the Romance, Slavic, Germanic and Indo-Iranian language families, the members of the Celtic family show considerable similarities among themselves in vocabulary, grammar, and so on. Centuries of work on the greater Indo-European family have already been done, insights and advances continue, and many resources exist for the Celtic conlanger and Bard-linguist to draw on. Proto-Celtic, the mother tongue of the Celtic languages, is also being reconstructed.
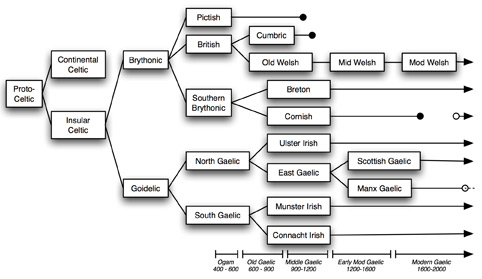 One early question to answer in birthing a Celtic conlang is Q or P. No, that’s not some password you have to know in order to gain admission to the Secret Circle of All Druidry (SCOAD), or a riddle posed by the Planetary High Holy Archdruid. P- and Q-Celtic are shorthand for a linguistic division that usefully divides the six living Celtic tongues into two groups of three, based on their treatment of the Indo-European *kw- in words like *kwetwores “four,” Proto Celtic *kwetwar-, with Irish ceathair, Gaelic ceithir, Manx kaire for the Q-side, and Breton pevar, Cornish pesvar and Welsh pedwar for the P-side. Of course, being next-door neighbors as well as cousins, the six languages also borrowed from each other through their centuries together, which delightfully muddies the waters of linguistic post-gnostication (“knowing after the fact,” like pro-gnostication, only not). Flip a coin, go with your gut, follow your own esthetic, pray, do a divination, or some idiosyncratic combo all your own.
One early question to answer in birthing a Celtic conlang is Q or P. No, that’s not some password you have to know in order to gain admission to the Secret Circle of All Druidry (SCOAD), or a riddle posed by the Planetary High Holy Archdruid. P- and Q-Celtic are shorthand for a linguistic division that usefully divides the six living Celtic tongues into two groups of three, based on their treatment of the Indo-European *kw- in words like *kwetwores “four,” Proto Celtic *kwetwar-, with Irish ceathair, Gaelic ceithir, Manx kaire for the Q-side, and Breton pevar, Cornish pesvar and Welsh pedwar for the P-side. Of course, being next-door neighbors as well as cousins, the six languages also borrowed from each other through their centuries together, which delightfully muddies the waters of linguistic post-gnostication (“knowing after the fact,” like pro-gnostication, only not). Flip a coin, go with your gut, follow your own esthetic, pray, do a divination, or some idiosyncratic combo all your own.
I’m going with P.
What else do we know about the Celtic Six as an initial orientation for a language maker? Quite a lot, actually. Here’s just a small sample: all six have a definite article (English “the”), but only one has an indefinite article (English “a, an”). Most have Verb-Subject-Object (VSO “Ate I breakfast”) as a common if not the dominant word order (English is SVO). All count with an old vigesimal system by twenties, as in French, where “eighty” is quatre-vingt “four twenties,” “ninety” is quatre-vingt dix “four twenties (and) ten,” and so on.
And the consonant mutations: no mutations and — sorry! — it’s just not Celtic! Sorta like a sundae without whipped cream, or a kielbasa slathered in coleslaw and mustard without the bun. In brief, depending on the preceding word, the initial consonant of a Celtic word changes in predictable ways. Here’s an example from Welsh:
Ei means “his.” It causes lenition of the consonant of a following word. Cath means “cat,” but when lenited after ei, the form is ei gath “his cat.
Ei also means “her” (and provides an example of how mutations can help distinguish words): ei “her” aspirates the consonant of a following word. Ei chath means “her cat.”
Eu means “their”: it doesn’t cause a mutation: eu cath is “their cat.”
It gets tricky because while the insular Celtic languages do all have mutations, their mutations behave differently from language to language. Here is Welsh again, now contrasted with Irish:
Welsh | Irish | English gloss
cath | cath | “cat”
ei gath | a chath | “his cat”
ei chath | a cath | “her cat”
eu cath | a gcath | “their cat” (Incidentally, not a typo: Irish gc- — like bp- and dt- — is pronounced g but also shows it is derived from an original c. Cool. Or ridiculous. Depending.)
/|\ /|\ /|\
May we remember you and your gifts, Bríd and Oghma: apt words, the praise of good things, and wisdom dark and bright.
To Brighid
(author unknown)
Brighid of the mantles, Brighid of the hearth fire,
Brighid of the twining hair, Brighid of the auguries,
Brighid of the fair face, Brighid of the calmness,
Brighid of the strong hands, Brighid of the kine.
Brighid, friend of women, Brighid, fire of magic,
Brighid, foster mother, Brighid, woman of wisdom,
Brighid, daughter of Danu, Brighid, the triple flame.
Each day and each night I call the descent of Brighid.
That the power of healing be within us,
That the power of poetry be within us,
That the power of shaping be within us,
In earth, and sky, and among all kindreds.
Kindle your flame in our heads, hearts and loins,
Make us your cup, your harp, your forge,
That we may heal, inspire and transform,
All in your honor, Brighid, font of blessing.
Brighid above us,
Brighid below us,
Brighid in the very air about us,
Brighid in our truest heart!
/|\ /|\ /|\
Images: Brigid’s Cross; Ogma.
Edited/updated 15 April 2015
 I’ve mentioned my obsession with Indo-European (IE) in previous posts, and given samples of a conlang I derived from IE and use in ritual. One of the many fascinations of this reconstructed language that’s the ancestral tongue of 3 billion people — half the people on the planet alive today — is the glimpses into the culture we can reconstruct along with the language. (Here’s a visual of the IE “family” and many of its members.) How, you thoughtfully ask, can we really know anything about a culture dating from some 6000 years ago – the very approximate time period when the speakers of the IE proto-language flourished? A good question — I’m glad you asked! – and one hotly contested by some with agendas to push – usually a nationalist or religious agenda intent on serving a worldview that excludes some group, worldview or idea. Hey kids, let’s define our club du jour by those we don’t let in!
I’ve mentioned my obsession with Indo-European (IE) in previous posts, and given samples of a conlang I derived from IE and use in ritual. One of the many fascinations of this reconstructed language that’s the ancestral tongue of 3 billion people — half the people on the planet alive today — is the glimpses into the culture we can reconstruct along with the language. (Here’s a visual of the IE “family” and many of its members.) How, you thoughtfully ask, can we really know anything about a culture dating from some 6000 years ago – the very approximate time period when the speakers of the IE proto-language flourished? A good question — I’m glad you asked! – and one hotly contested by some with agendas to push – usually a nationalist or religious agenda intent on serving a worldview that excludes some group, worldview or idea. Hey kids, let’s define our club du jour by those we don’t let in!
But the most reasonable and also plausible answer to the question of IE language and culture is also simpler and less theatrical. Indo-European is the best and most thoroughly reconstructed proto-language on the planet — and it’s true there’s much still to learn. But after over two hundred years of steady increases in knowledge about human origins and of thoroughly debated and patient linguistic reconstruction, the techniques have been endlessly proven to work. And if a series of words that converge on a cultural point or practice can be reconstructed for IE, then the cultural practice or form itself is also pretty likely. Notice I don’t say merely a single word. Yes, to give a modest example, IE has the reconstructed word *snoighwos “snow” (the * indicates a reconstruction from surviving descendants — see footnote 1 below for a sample) – and that possibly suggests a region for an IE “homeland” that is temperate enough to get snow. After all, why have a word for a thing that’s not part of your world in any way? But wait — there’s more!
Here’s an uncontested (note 2) series of reconstructions – *pater, *mater, *sunu, *dukter, *bhrater and *swesor – all pointing to an immediate family unit roughly similar to our “nuclear family,” with father, mother, son, daughter, brother and sister all in place. It’s fairly safe on the basis of this cluster of reconstructed words – and others, if you still doubt, can be provided in painfully elaborate detail – that with a high degree of probability, an IE family existed all those millennia ago that would also be recognizable in modern times and terms.
[Side note: almost every reconstructed IE word listed in this post has a descendant alive in modern English. Want proof? Post a comment and I’ll be happy to provide a list!]
 Things understandably get touchier and more contentious when we move on to words and ideas like *deiwos “god”; *nmrtya “immortality”; *dapnos “potlatch, ritual gift-exchange”; *dyeu + *pater “chief of the gods” (and Latin Jupiter); *sepelyo– “perform the burial rites for a corpse”; and a few whole phrases like *wekwom tekson, literally “weaver of words, poet” and *pa- wiro-peku, part of a prayer meaning something like “protect people and cattle.”
Things understandably get touchier and more contentious when we move on to words and ideas like *deiwos “god”; *nmrtya “immortality”; *dapnos “potlatch, ritual gift-exchange”; *dyeu + *pater “chief of the gods” (and Latin Jupiter); *sepelyo– “perform the burial rites for a corpse”; and a few whole phrases like *wekwom tekson, literally “weaver of words, poet” and *pa- wiro-peku, part of a prayer meaning something like “protect people and cattle.”
What else can we conclude with considerable confidence about the IE peoples? Many lived in small economic-political units governed by a *reg– “king, chieftain” and lived in *dom– “houses.” Women *guna, *esor left their families at marriage and moved to live with their husbands *potis, *ner, *snubhos. A good name *nomen mattered then just as it does today – even with social media both exalting and trashing names with sometimes dizzying speed – though small-town gossip always filled and fills that role quite well, too. Heroes dominated the tales people told round household and ceremonial fires *pur, *ogni in the village *woikos, *koimos at night *nokwti. The most powerful and famous *klewes– heroes succeeded in slaying the serpent or monster of chaos: *oghwim eghwent “he slew the serpent” and thereby earned *klewos ndhghwitom “undying fame” (note 3). Special rites called for an *asa altar and offerings *spond-, because the universe was a place of an ongoing re-balancing of forces where the cosmic harmony *rti, *rta needed human effort to continue.
With Thanksgiving in the wings, it’s a good time for reflection (is it ever not?). Ways of being human have not changed as much as we might think or fear or be led to believe. Family, relationships, good food and drink, a home, meaningful work, self-respect – these still form the core of the good life that remains our ideal, though its surface forms and fashions will continue to shift, ebb and flow. Hand round the *potlom cup and the *dholis, the portion each person shares with others, so that all may live, and we can still do as our ancestors did: give thanks *gwrat– and praise for the gift *donom of life *gwita.
/|\ /|\ /|\
1. Linguistic reconstruction involves comparing forms in existing and recorded languages to see whether they’re related. When you gather words that have a strong family resemblance and also share similar or related meanings, they help with reconstructing the ancestral word that stands behind them, like an old oil portrait of great-great-great grandma in the hallway. Some descendant or other probably still walks around with her characteristic nose or brow or eyes, even if other details have shifted with time, marriage — or cosmetic surgery.
For *snoighwos, a sample of the evidence includes English snow, Russian snegu, Latin nix, niv-, Sanskrit sneha-, and so on. The more numerous the survivals in daughter languages, the more confident the reconstruction usually is. After a while you see that fairly consistent patterns of vowels and consonants begin to repeat from word to word and language to language, and help predict the form a new reconstruction could take.
A handful of reconstructed words have descendants in all twelve (depending on who does the counting) of the main IE family groups like Italic (Latin, Oscan, Umbrian, all the Romance languages, and others), Celtic (Irish, Welsh, Breton, Manx, etc.), Germanic (German, English, Dutch, Icelandic, Norwegian, Frisian, Swedish, Gothic, etc.), Baltic (Latvian, Lithuanian, Prussian), Slavic (Russian, Serbian, Polish, Czech, Ukrainian, Slovene, Polabian, Old Church Slavonic, etc.), Greek (Doric, Macedonian, Attic, etc.), Tocharian (A and B), and Indo-Iranian (Sanskrit, Pali, Avestan, Bengali, Hindi, Urdu, Sindhi, Kashmiri, Dari, Pashto, Farsi, Baluchi, Gujerati, etc.) and so on, to name roughly half of the families, but nowhere near all the members, which number well over 100, not counting dialects and other variants.
2. “Uncontested” means that words with approximately these forms and meanings are agreed on by the overwhelming majority of scholars. If you dip into Indo-European linguistics journals and textbooks, you’ll often see algebraic-looking reconstructions that include details I exclude here — ones having to do with showing laryngeals, stress, vowel length and quality, etc. indicated by diacritics, superscripts and subscripts.
3. Even without the details mentioned in note 2 above, some reconstructions can still look formidably unpronounceable: I challenge any linguist to give three consecutive oral renderings of the second element in the reconstructed phrase *klewos ndhghwitom! The point to remember is that these are usually cautious reconstructions. They generally “show what we know.” Vowels tend to be much more slippery and fickle than consonants in most languages, and so they’re also less often completely clear for IE than the consonantal skeleton is. Several people, me among them, have worked on versions of “Indo-European for daily use”!
Images: Mallory; Indiana Jones the linguist.
Corrected 18 Dec. 2014
It’s almost here: Halloween, All Hallows Eve, Samhain/Samhuinn, Dia del los Muertos, Day of the Dead. Whatever you call it, it’s one of the most unusual festivals in the calendar. In this post I want to take a different tack, exploring history at least somewhat removed from the usual Christian-Pagan fireworks that continue to pop off annually around this time. Because the Druid-pleasing answer* to “Is it Christian?” and “Is it Pagan?” is “Yes.” What matters more, I hope, is what that can mean for us today.

A recent (Tues., Oct 28) issue of the U.K.’s Guardian newspaper features an article on Halloween by British historian Ronald Hutton, who’s well known in Druid circles both for the quality and thorough documentation of his historical work and also his interest in Druidry. Among many other points, Hutton addresses the impression, widespread in Great Britain, that Halloween’s an import from the U.S. It’s not, of course, being instead as English as Monty Python and Earl Grey (and later, as Irish as the Famine, and Bailey’s Irish Cream). Hutton’s observations suggest a connection I’d like to make in this post, in keeping with this time of year. Hence my title, which will become clear in a moment. Just bear with me as I set the stage.
November, rather unimaginatively named “Ninth Month” (Latin novem), was called in Anglo-Saxon Blodmonath, the “blood month” — not for any “evil, nasty and occult” reasons beloved of today’s rabble-rousers, but for the simple fact this was the month for the slaughter of animals and preservation of meat for the coming season of darkness and cold.
Hutton observes that the ancestor to modern Halloween:
… was one of the greatest religious festivals of the ancient northern pagan year, and the obvious question is what rites were celebrated then.
The answer to that is that we have virtually no idea, because northern European pagans were illiterate, and no record remains of their ceremonies. The Anglo-Saxon name for the feast comes down to an agricultural reality, the need to slaughter the surplus livestock at this time and salt down their meat, because they could not be fed through the winter. A Christian monk, Bede, commented that the animals were dedicated to the gods when they were killed, but he did not appear to know how (and they would still have been eaten by people).
Hutton proceeds to examine how we can nevertheless reconstruct something of that time and its practices through careful research. As a Janus-faced holiday, Halloween marked the fullness and completion of the harvest and return home of warriors and travelers — a time to celebrate. It also marked the coming of the hardest season — winter: cold, dark, often miserable and hungry, and sometimes fatal. People then measured their ages not in years but in winters — how many you’d survived. Hutton eloquently conveys all this — do read his article if you have time.
And because so much of North America bears the imprint of English culture, I want to peer at one particular autumn, and the Hallowed Evening that year, in England 948 years ago. It’s 1066, a good year at the outset, as historian David Howarth paints it** in his wonderfully readable 1066: The Year of the Conquest. A year, strangely enough, both like and unlike our own experience so many generations later in 2014:
It was not a bad life to be English when the year began: it was the kind of life that many modern people vainly envy. For the most part, it was lived in little villages, and it was almost completely self-sufficient and self-supporting; the only things most villages had to buy or barter were salt and iron. Of course it was a life of endless labour, as any simple life must be, but the labour was rewarded: there was plenty to eat and drink, and plenty of space, and plenty of virgin land for ambitious people to clear and cultivate. And of course the life had sudden alarms and dangers, as human life has had in every age, but they were less frequent than they had ever been: old men remembered the ravages of marauding armies, but for two generations the land had been at peace. Peace had made it prosperous; taxes had been reduced; people had a chance to be a little richer than their forefathers. Even the weather was improving. For a long time, England had been wetter and colder than it normally is, but it was entering a phase which lasted two centuries when the summers were unusually warm and sunny and the winters mild. Crops flourished, and men and cattle throve. Most of the English were still very poor, but most of the comforts they lacked were things they had never heard of.
Howarth’s account continues, vivid in detail; he chooses the small town of Little Horstede near Hastings that dates from Saxon times for his focus, to examine the immediate and later impact of the Norman Conquest.

Harold in the Bayeux tapesty, with a hawk
By early autumn of the year, things still looked promising for the English. True, their king Harold Godwinson, new to the throne just that past January, faced a dispute with the Norman duke William over the succession after the late king Edward passed. But Harold was Edward’s brother-in-law, he apparently had the late king’s deathbed promise of the throne, he was unanimously elected by the Witan (the English council of royal advisers), and he was a crowned and fully invested king as far as the English were concerned.
He was also proving to be a competent leader and warrior. When an invading army of some 7000*** Norwegians under Harald Hardrada and Harold’s exiled brother Tostig landed in the Northeast of England, Harold rode north in force, covering the 180 miles between London and Yorkshire in just four days, meeting and defeating the Norwegians on September 25 in the Battle of Stamfordbridge. The peace that the English had enjoyed was tested, but as word spread of this English victory, you can imagine the relief and the sense that all might well continue as it had for decades now. The rich harvest of 1066 went forward, and plans could proceed for the annual All Hallows celebration.

Swithun (d. 862), bishop, later saint, of Winchester
England was by this time thoroughly Christian (see St. Swithun, left), though folk memories of older practices doubtless persisted, mixed with a fair helping of legend and fantasy and uneven religious instruction from the local priests. The Christian retrofitting of Pagan holidays, holy sites and practices is well documented, and hardly unique to Christianity — the same thing occurs worldwide as religions encounter each other and strive for dominance or co-exist to varying degrees. To name just a few examples, take for instance Roman polytheism and many faiths in the lands of the ancient Empire, with Roman priests adding one more deity statue to the crowd for each new god they encountered, including the current emperor of course (with most peoples acquiescing happily except for those odd Jewish monotheists and their bizarre prohibition against such images!); Buddhism and the emergence of the Bon faith in Tibet; Shinto and Buddhism in Japan; and mutual influence between Islam, Sufism, and older practices like the Yazidi faith in the Middle East.
In his Guardian article on Halloween, Hutton notes:

All Saints Day, Oswiecim, Poland
It is commonly asserted that the feast was the pagan festival of the dead. In reality feasts to commemorate the dead, where they can be found in ancient Europe, were celebrated by both pagans and early Christians, between March and May, as part of a spring cleaning to close off grieving and go forth into the new summer. On the other hand, the medieval Catholic church did gradually institute a mighty festival of the dead at this time of year, designating 1 November as the feast of All Saints or All Hallows, initially in honour of the early Christian martyrs, and 2 November as All Souls, on which people could pray for their dead friends and relatives. This was associated with the new doctrine of purgatory, by which most people went not straight to hell or heaven but a place of suffering between, where their sins were purged to fit them for heaven. It was also believed that the prayers of the living could lighten and shorten their trials, as could the intercession of saints (which is why it was good to have all of those at hand). The two new Christian feasts were, however, only developed between the ninth and the twelfth centuries, and started in Germanic not Celtic lands.
Yet all was not peace in England. The triumph that was the Battle of Stamfordbridge proved short-lived. Disturbing rumors kept arriving of William assembling an army of invasion across the English Channel on the shores of Normandy, in fact ever since January when Harold received the crown. The English king began preparations for defense. Yet as the days and months passed, and the good weather for such crossings steadily diminished as all of September and then early October came and went without incident, most people began to relax. England would enjoy a breathing space for this winter at least. Whatever might happen next spring, this late in the year no one chanced the storms, fog and rough water, least of all a large army that would have to arrive by boat.
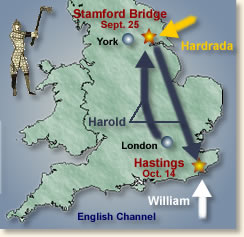 Yet William and his invasion force did just that. After weeks of bad weather, the wind finally shifted to favor the Norman leader, and he and his men set sail on September 27. When word came to the English king of the Norman landing, with ships and troops on the southern shore of England, king Harold and company rode back south, already weary from one major battle, right into another.
Yet William and his invasion force did just that. After weeks of bad weather, the wind finally shifted to favor the Norman leader, and he and his men set sail on September 27. When word came to the English king of the Norman landing, with ships and troops on the southern shore of England, king Harold and company rode back south, already weary from one major battle, right into another.
Careful excavation, study of contemporary accounts, and site visits mean that resources like the Eyewitness to History website can give us a portrait like this:
Harold rushed his army south and planted his battle standards atop a knoll some five miles from Hastings. During the early morning of the next day, October 14, Harold’s army watched as a long column of Norman warriors marched to the base of the hill and formed a battle line. Separated by a few hundred yards, the lines of the two armies traded taunts and insults. At a signal, the Norman archers took their position at the front of the line. The English at the top of the hill responded by raising their shields above their heads forming a shield-wall to protect them from the rain of arrows. The battle was joined.
Contemporary accounts record how the two armies fought all day, until Harold was dispatched with an arrow through one eye. Shortly after that, the disabled king was cut down by Norman warriors, and England’s fate turned.
Years later the Bayeux Tapestry commemorated a version of the event. But of course at the time there was no Twitter feed, no broadcast of news minutes after it happened by correspondents on the scene. No Fox News and CNN to digest and sort through the implications according to the politics of the day. Word of the battle and what it might mean would take weeks to spread, rippling northward from the coast where the first battles took place. For much of England, the Hallowed Evening, the All Saints Day of 1066 came and went without change.
At this distance, and without knowing the details, most of us may naturally have the impression Hastings was decisive. King Harold dead, battle won, QED. From there, we assume, William advanced toward London, accepted the grudging fealty of a defeated people, and after maybe quelling a few sparks of resistance or rebellion, took firm control of the throne and nation and ruled for the next 21 years, until his death in 1087.
Except not. True, William was crowned king in Westminster on Christmas Day 1066. But the following years brought their own troubles for the Norman king. Here’s the Wikipedia version (accessed 10/30/14; endnotes deleted):
Despite the submission of the English nobles, resistance continued for several years. William left control of England in the hands of his half-brother Odo and one of his closest supporters, William FitzOsbern. In 1067 rebels in Kent launched an unsuccessful attack on Dover Castle in combination with Eustace II of Boulogne. The Shropshire landowner Eadric the Wild, in alliance with the Welsh rulers of Gwynedd and Powys, raised a revolt in western Mercia, fighting Norman forces based in Hereford. These events forced William to return to England at the end of 1067. In 1068 William besieged rebels in Exeter, including Harold’s mother Gytha, and after suffering heavy losses managed to negotiate the town’s surrender. In May, William’s wife Matilda was crowned queen at Westminster, an important symbol of William’s growing international stature. Later in the year Edwin and Morcar raised a revolt in Mercia with Welsh assistance, while Gospatric, the newly appointed Earl of Northumbria, led a rising in Northumbria, which had not yet been occupied by the Normans. These rebellions rapidly collapsed as William moved against them, building castles and installing garrisons as he had already done in the south. Edwin and Morcar again submitted, while Gospatric fled to Scotland, as did Edgar the Ætheling and his family, who may have been involved in these revolts. Meanwhile Harold’s sons, who had taken refuge in Ireland, raided Somerset, Devon and Cornwall from the sea.
Pacification, oddly enough, usually involves violence.
Ideologies and politics trouble us this Halloween just as they did 948 years ago, on a misty green island off the continent of western Europe.
Centuries later, as blended Norman and English cultures formed a new unity, the Protestant Reformation which swept much of Great Britain blotted out the doctrine of purgatory and the practice of prayer for saintly intercession. But as Hutton notes, Halloween “survived in its old form in Ireland, both as the Catholic feast of saints and souls and a great seasonal festival, and massive Irish emigration to America in the 19th century took it over there.”
In fact, having made this a citation-heavy post anyway, I’ll give Hutton nearly the last word, which is also his last word in his article:
In the 20th century [Halloween] developed into a national festivity for Americans, retaining the old custom of dressing up to mock powers of dark, cold and death, and a transforming one by which poor people went door to door to beg for food for a feast of their own, morphing again into the children’s one of trick or treat. By the 1980s this was causing some American evangelical Christians to condemn the festival as a glorification of the powers of evil (thus missing all its historical associations), and both the celebrations and condemnations have spilled over to Britain.
On the whole, though, the ancient feast of Winter’s Eve has regained its ancient character, as a dual time of fun and festivity, and of confrontation of the fears and discomforts inherent in life, and embodied especially in northern latitudes by the season of cold and dark.
There’s a worthwhile Conquest. “Is it Pagan?” “Is it Christian?” Let’s ask “Is it holy?”
/|\ /|\ /|\
Images: jack-o-lanterns; Harold on the tapestry; St. Swithun; battle map; All Saints Day, Oswiecim, Poland, 1984.
*Rather than dualities and polar opposites, ternaries and triples permeate Druidry. As J. M. Greer observes,
Can anything as useful be done with the three elements of Iolo’s Druid philosophy, or for that matter with the four medieval or five Chinese elements?
Nwyfre, gwyar, and calas make poor guides to physics or chemistry, to be sure. Their usefulness lies elsewhere. Like other traditional elemental systems, the three Druid elements make sense of patterns throughout the universe of our experience. Tools for thinking, their power lies in their ability to point the mind toward insights and sidestep common mistakes.
Take the habit, almost universal nowadays, of thinking about the universe purely in terms of physical matter and energy. This works fairly well when applied in certain limited fields, but it works very badly when applied to human beings and other living things. Time and again, well-intentioned experts using the best tools science has to offer have tried to tackle problems outside the laboratory and failed abjectly. Rational architecture and urban planning, scientific agriculture and forestry, and innovative schemes for education and social reform often cause many more problems than they solve, and fail to yield the results predicted by theory.
Why? The theoreticians thought only of gwyar and calas, the elements of change and stability, expressed here as energy and matter. They left something out of the equation: nwyfre, the subtle element of life, feeling, and awareness. They forgot that any change they made would cause living things to respond creatively with unpredictable changes of their own.
In every situation, all three elements need to be taken into account. They can be used almost as a checklist. What is the thing you’re considering, what does it do, and what does it mean? What will stay the same, what will change, and what will respond to the change with changes of its own? This sort of thinking is one of the secrets of the Druid elements.
**Howarth, David. 1066: The Year of the Conquest. Penguin Books, 1981, pgs. 11-12.
***A conservative figure — estimates range as high as 9000.
 Some of you may recall a minor kerfluffle from the Christian Right a decade or so ago, when then Anglican Archbishop Rowan Williams joined the Welsh Gorsedd of Bards and appeared in — gasp! — “pagan” Druid robes and hood. One of the many ironies of that moment and others’ reactions to it is that of all Druid groups, the Welsh Gorsedd is among the most secular and the least woo-woo (a highly technical sociological term).
Some of you may recall a minor kerfluffle from the Christian Right a decade or so ago, when then Anglican Archbishop Rowan Williams joined the Welsh Gorsedd of Bards and appeared in — gasp! — “pagan” Druid robes and hood. One of the many ironies of that moment and others’ reactions to it is that of all Druid groups, the Welsh Gorsedd is among the most secular and the least woo-woo (a highly technical sociological term).
So here’s a worthy sequel: an excerpt from a 2009 lecture Williams gave titled “The Climate Crisis — a Christian Response.” During his talk he offers Druidic perspectives:
I once suggested that one necessary contribution to a better awareness of these issues was to make sure we went out of doors in the wet from time to time (a suitable lesson from Noah…), and – if we haven’t got gardens of our own – make sure we took opportunities of watching the changing of the seasons on the earth’s surface. This may seem trivial compared with the high drama of ‘saving the world’; but if this analysis is correct, our underlying problem is being ‘dissociated’, and we ought to be asking constantly how we restore a sense of association with the material place and time and climate we inhabit and are part of.
A transcript appears on the link page — it’s worth skimming for additional insights like this, a thoughtful and mature Christian grappling with the same realities we all face, and feeling his way into a diagnosis that accords with earth-centered insights and experiences — one that also doesn’t deny Christian wisdom either.
/|\ /|\ /|\
Image: Rowan Williams/BBC News.
Our bodies already know the Goddess – this is our oldest magic.
I relied on this insight in planning for the workshop at this year’s East Coast Gathering, whose theme was “Connecting with the Goddess.”
/|\ /|\ /|\
Goals and plans I had for the workshop:
The heart of the workshop is a hands-on look at various ways to make a physical book/scroll/altar object that explores/invites/incorporates ritual, ogham/runes, art, prayer, poems, questions, magic and daydreaming into a concrete “link” to the Goddess as we experience Her — or desire to experience Her. Think “book” as “portable paginated/folding/roll-up ongoing altar-in-process.” I’ll talk about inspiration, nudges, hints and ways to listen, inviting and hoping for participant sharing and input! The seed for the workshop comes out of the fact that I’m a prime example of somebody who doesn’t have a consistent Goddess practice (though She’s seeing to it that’s shifting, too), but when She wants my attention, She gets it, like with this book, and workshop.
It’s probably a good thing we don’t always hear how ambitious we sound. Young or old, you eventually learn to deal with the inevitable gap between vision and manifestation. If you’ve managed to hold on to any of that original and wonderful idealism of youth, you also realize that the gap isn’t a reason to despair, or to dispense with vision, but rather a sign of just how important vision is.
The physical world, so important for manifestation, by its nature tends to lag behind the swiftness with which vision can appear. But that lag is precisely part of this world’s immense value: its inertia and density allow for greater permanency and resistance to change, so that we can experience the results of vision over time — and fine-tune it if we choose. Unlike in dream, where the subtle stuff of vision or imagination can wisp away so quickly, physical manifestation tries to linger.
/|\ /|\ /|\
The Goddess is generous. Or alternatively, if you prefer the cynical version, I belong to the OCD Order of Druids. Creativity, as the saying goes, is messy. I over-planned for the workshop, ending up with far more material than any mortal could begin to do justice to in a mere hour, and this post is my penance, or confession. Or further indulgence. And maybe — in the way it often arrives when we’re not paying attention, even in spite of ourselves — a spark of awen.
/|\ /|\ /|\
 “Creating A Goddess Book,” with focus on “book” in order to free it from the psychological shrine many Druids, and Pagans generally, tend to put books in. Instead of paper, a book of leather, or metal, or cloth — individual sheets, or a single longer scroll. A nudge to try out the qualities of other substances than paper, than the admittedly inviting blank books on sale in chain bookstores, or even Ye Friendlie Lokal Paygan Shoppe.
“Creating A Goddess Book,” with focus on “book” in order to free it from the psychological shrine many Druids, and Pagans generally, tend to put books in. Instead of paper, a book of leather, or metal, or cloth — individual sheets, or a single longer scroll. A nudge to try out the qualities of other substances than paper, than the admittedly inviting blank books on sale in chain bookstores, or even Ye Friendlie Lokal Paygan Shoppe.
Each workshop participant received a packet to practice with, consisting of a rectangle (approx. 3″ x 4″) of vegetable-cured leather and a similar-sized rectangle of .019″ aluminum, wrapped in a larger swath of canvas cut from a shop drop-cloth from Home Depot. A wood- and leather-burning tool, a few screwdrivers, some markers of various kinds, a few words about inspiration and the importance of working to manifest things on the physical plane as one powerful way to connect with the Goddess. Suggestions for inscribing/writing/ incising a short prayer, vow, magical name, etc. Reference tables of Ogham and runes for those who wanted to inscribe words with some privacy, as a personal meditation. I pointed out that you could cut all three materials with kitchen scissors. Besides the wood-burner, no fancy tools required. Then I shut up and let participants have at the materials. Done!

Hex Nottingham’s leather and metal “pages” — photo courtesy Hex Nottingham
Except for the next flash of inspiration in the planning process, which would not let go: a “Nine-Fold Star of the Goddess” you can try out here at one of several websites that illustrate the steps.
/|\ /|\ /|\
A sampling, with some commentary and additions, from the workshop handout:
“Spirit must express itself in the world of matter or it accomplishes nothing. Insights of meditation and ceremony gain their full power and meaning when reflected in the details of everyday life.” — J. M. Greer, The Druidry Handbook, p. 138.
This world, here, is the realm of mystery. Spirit is simple — it’s this world that’s so surprising and complex in its changes and ripples, its folds and spirals and timings. Make something, I tell myself, labor with the body, and then I can often approach the Goddess more easily, dirt under my fingernails, sweat on my face. She likes bodies. I’m the one who keeps forgetting this, not her.
“Work with a Goddess long enough and you learn to hear Her call. You learn to pick her voice out above the noise of contemporary society, above the words of teachers and friends, and even above your own thoughts and feelings. Sometimes what you hear is not what you expect.” — John Beckett, “A Rite of Sacrifice,” Mar. 4, 2014.
“Shaper, you have made and shaped me. Honor and serenity are yours. I am your garment, you the indwelling spirit. Work with me in everything I do, that all may know you. Energizer, quicken me. Measurer, clear my path. Protector, guard me safely. Initiator, take my hand. Challenger, transform me. Savior, be my help. Weaver, make my pattern bright. Preserver, heal me. Empowerer, make me wise.” — adapted from Caitlin Matthews, Elements of the Goddess, p. 118.
Rilke’s fragment, a whole meditation in itself, or a daily morning prayer.
Oh, I who long to grow,
I look outside myself, and the tree
inside me grows.
— Rainer Maria Rilke
And Larkin’s poem “Water”:
Water
If I were called in
To construct a religion
I should make use of water.
Going to church
Would entail a fording
To dry, different clothes;
My liturgy would employ
Images of sousing,
A furious devout drench,
And I should raise in the east
A glass of water
Where any-angled light
Would congregate endlessly.
— Philip Larkin
After delighting in this poem, make an exercise of it. Choose one of the elements. It can be water, as in the poem, or one of the others. Finish the sentence: “If I were called in to construct a _____, I should make use of [element].” Keep going: a series of statements, a meditation on the one you just wrote, a free association. Whatever gets you putting words down. You can try this over several days with all the elements, or at a different pace, if you’re working with the elements on your own.
The ECG schedule this year put the Goddess Book workshop immediately after Thursday’s Opening Ritual, so people arrived still bubbling from the ceremonial jump-start for the weekend.
“In every world, in every form, in every way, I am near you, I uphold you, I comfort you, I guide you, I deliver you from each limitation until my freedom is yours. Your body is my chalice, your heart my echo, your form my shadow, your pulse my footstep, your breath my passing.” — from my own Goddess book.
/|\ /|\ /|\

1. Once you hold the Star of the Goddess in your hand, write the names of the four elements and Spirit, one near each of the points. Complete this step before reading further.
2. Which elements sit on either side of Spirit? Contemplate on their positions there. Are they elements that help support your spiritual life? Are they especially active? Are these the elements that need extra attention and balance?
3. Consider a section in your Goddess book for vows: experiment with them, not as harsh, unyielding obligations, but as tools for studying resolve, testing experience, practicing manifestation of your intent, and so on. They need not be “public” – write them in ogham, runes, etc. Start small and easily achievable.
/|\ /|\ /|\
Dedicating a Goddess Book: Blood, sweat, tears, spit, etc. can mark our books with our earthiness: a commitment to be honest with the Goddess about our path, its ups and downs, to remember her presence with us, and to acknowledge what we need, what we doubt, what we’re willing to work for – whatever feels right to include. Make a ritual of it. Do it quietly, simply, without fanfare, with silence making its own ritual. Or call out all the stops, bells and whistles. Then dance, feast and celebrate.
/|\ /|\ /|\
Allow a Goddess book — it could be a single sheet or “page” specifically intended for this purpose — to return slowly to the elements on an outdoor altar. Or bury it in the Mother’s good earth. Thus is the vow fulfilled that the Mother takes into Herself, as She will take all things back in time, and return them again.
“All things are holy to you. This book like all things lies among the faces you show to me; may I learn from you daily, drink deep from your well, and body you forth as your child.” — from my Goddess book.
/|\ /|\ /|\
A small ritual. Take a few deep breaths. Sing the awen, or other name or word that grounds and focuses you. Holding your cupped hands in front of you, say: “I make this altar for the Goddess, a space where she may act in my life.”
Holding the Star, or your journal, or other ritual object meaningful to you, or nothing else at all, ask yourself: What specific space or doorway exists in my life for the Goddess to manifest or to act in? Pay attention to hints, images and answers as they come.
/|\ /|\ /|\
And again: Our bodies already know the Goddess – this is our oldest magic.
/|\ /|\ /|\
Images: ogham; star.
 Not responsible for spontaneous descent of Awen or manifestation of the Goddess. Unavailable for use by forces not acting in the best interests of life. Emboldened for battle against the succubi of self-doubt, the demons of despair, the phantoms of failure. Ripe for awakening to possibilities unforeseen, situations energizing and people empowering.
Not responsible for spontaneous descent of Awen or manifestation of the Goddess. Unavailable for use by forces not acting in the best interests of life. Emboldened for battle against the succubi of self-doubt, the demons of despair, the phantoms of failure. Ripe for awakening to possibilities unforeseen, situations energizing and people empowering.
Catapulted into a kick-ass cosmos, marked for missions of soul-satisfying solutions, grown in gratitude, aimed towards awe, mellowed in the mead of marvels. Optimized for joy, upgraded to delight, enhanced for happiness. Witness to the Sidhe shining, the gods gathering, the Old Ways widening to welcome.
 Primed for passionate engagement, armed for awe-spreading, synchronized for ceremonies of sky-kissed celebration. Weaned on wonder, nourished by the numinous, fashioned for fabulousness. Polished for Spirit’s purposes, dedicated to divine deliciousness, washed in the waters of the West, energized in Eastern airs, earthed in North’s left hand, fired in South’s right. Head in the heavens, heart with the holy, feet in flowers, gift of the Goddess, hands at work with humanity. Camped among the captives of love, stirred to wisdom in starlight, favored with a seat among the Fae, born for beauty, robed in the world’s rejoicing, a voice in the vastness of days.
Primed for passionate engagement, armed for awe-spreading, synchronized for ceremonies of sky-kissed celebration. Weaned on wonder, nourished by the numinous, fashioned for fabulousness. Polished for Spirit’s purposes, dedicated to divine deliciousness, washed in the waters of the West, energized in Eastern airs, earthed in North’s left hand, fired in South’s right. Head in the heavens, heart with the holy, feet in flowers, gift of the Goddess, hands at work with humanity. Camped among the captives of love, stirred to wisdom in starlight, favored with a seat among the Fae, born for beauty, robed in the world’s rejoicing, a voice in the vastness of days.

Knowing, seeing, sensing, being all this, you can never hear the same way again these two words together: “only human”!
/|\ /|\ /|\
Images: three from a sequence taken yesterday, 3 Oct 14, on a blessed autumn day in southern Vermont two miles from my house.

Camp Netimus path — photo courtesy of Carolyn Batz
[Here are reviews of ECG 12 and ECG 13.]
East Coast Gathering (ECG) ’14 just celebrated its fifth Alban Elfed/ autumn equinox in the wooded hills of NE Pennsylvania. Along with this year’s theme of “Connecting to the Goddess,” 114 people reconnected to each other and the land, the lovely land. New participants and old remarked on the kindness of place, the welcoming spirit of Netimus, a flourishing girls’ camp founded in 1930 that now plays host off-season to other groups, too.
[For another perspective on this year’s Gathering, visit and read John Beckett’s excellent blog “Under the Ancient Oaks.”]
After a wet summer in the Northeast, the camp showed richly green — mosses, lichens, leaves and light all caressing the gaze wherever you looked. And keeping to our tradition of inviting guests from the U.K., we welcomed Kristoffer Hughes of the Anglesey Druid Order and returning guests Penny and Arthur Billington, this time accompanied by their daughter Ursula, a mean fiddler with Ushti Baba (Youtube link).
For me what distinguished this year’s Gathering, my fourth, was the pure joy in so many people’s faces. And it just grew over the weekend. Over and around travel fatigue, colds, tricky schedules and stresses and waiting commitments — everything — they didn’t matter: the tribe was together again. To you all (from an interfaith week I participated in): “Thank you for the blessings that you bring. Thank you for the blessings that you are.”
/|\ /|\ /|\
Dana’s Goddess Shrine in a tent on our ritual field was also a wonderful addition and a focus for many of us.

Goddess Shrine — photo courtesy of Nadia Chauvet
Natural offerings accumulated over the weekend — mosses, lichen-streaked stones, acorns, leaves, a small sun-bleached animal skull — were returned to Netimus, and the other items packed up for next time. A workshop I led, on making a Goddess Book, drew me back to the shrine several times for reflection and inspiration. (Here’s the link I mentioned at Camp to a video on making the “Nine-Fold Star of the Goddess” — seeing the steps in 3D should help make my hand-drawn images on the handout easier to read once you practice a few times. A series of divinations and meditations were to follow which I never got to in the workshop — though over-planning is usually better than under-planning. Material for a subsequent post!)
I continue to meditate on a surprising goddess experience during Penny’s workshop, which I may be able to write about in an upcoming post. One of the potencies of such gatherings of like-minded people is the spiritual crucible that can form and catalyze discoveries in ways not always easily accessible in solitary practice.
/|\ /|\ /|\
Our fire-keepers outdid themselves this year, building enormous pyres (one with an awen worked in wood) to provide the centerpiece of each evening’s gathering after supper, workshops and initiations had concluded.

Awen bonfire ready — photo courtesy Nadia Chauvet

evening bonfire — photo courtesy John Beckett
As always it’s people who carry the spirit of Druidry. Here as they tour New York City, just prior to the camp, are Kristoffer, Renu, Ursula, Penny and Arthur.

Renu with our UK guests in NY — photo courtesy Renu Aldritch
I’ll return to A Druid Way (and the fourth post in the “American Shinto” series) when I get back from the annual East Coast Gathering (ECG) this coming weekend. This year’s 5th ECG shares in some of the energy of the OBOD 50th anniversary earlier this summer in Glastonbury, UK. For many U.S. Druids, the Gathering is the principal festival event of the year, a chance to renew old friendships, enter sacred time and space, and reaffirm ties to the special landscape of Camp Netimus in NE Pennsylvania. This year’s Gathering theme is “Connecting with the Goddess.”
In the interim, here are three images from last year’s Gathering — a visual invocation of the Alban Elfed/Autumnal Equinox energies of the Camp.

Camp Netimus sign — photo courtesy Krista Carter

Steps up to fire circle from Main Lodge — photo courtesy of Wanda GhostPeeker

The evening bonfire
[Related posts: Shinto & Shrine Druidry 1 | 2 | 3 || Shinto — Way of the Gods || Renewing the Shrine 1 | 2 || My Shinto 1 | 2 ]
Below are images from our recent visit to Spirit in Nature in Ripton, VT, some eight miles southeast of Middlebury as the crow flies. An overcast sky that day helped keep temperature in the very comfortable low 70s F (low 20s C). At the entrance, Spirit in Nature takes donations on the honor system. The website also welcomes regular supporters.

As an interfaith venture, Spirit in Nature offers an example of what I’ve been calling Shrine Druidry, one that allows — encourages — everyone into their own experience. Everyone who chooses to enter the site starts out along a single shared path.

The labyrinth helps engage the visitor in something common to many traditions worldwide: the meditative walk. The labyrinth imposes no verbal doctrine, only the gentle restraint of its own non-linear shape on our pace, direction and attention.

Beyond the labyrinth, a fire circle offers ritual and meeting space. Here again, no doctrine gets imposed. Instead, opportunity for encounter and experience. Even a solitary and meditative visitor can perceive the spirit of past fires and gatherings, or light and tend one to fulfill a present purpose.

Beyond the circle, the paths begin to diverge — color-coded on tree-trunks at eye-level — helpful in New England winters, when snow would soon blanket any ground-level trail markers. When we visited, in addition to the existing paths of 10 traditions, Native American and Druid paths branched off the main way, too new to be included on printed visitor trail maps, but welcome indicators that Spirit in Nature fills a growing need, and is growing with it.

The Druid Prayer captures a frequent experience of the earth-centered way: with attention on stillness and peace, our human interior and exterior worlds meet in nature.

The trails we walked were well-maintained — the apparently light hand that brings these trails out of the landscape belies the many hours of volunteer effort at clearing and maintenance, and constructing bridges and benches.

A bench, like a fire pit and a labyrinth, encourages a pause, a shift in consciousness, a change, a dip into meditation — spiritual opportunities, all of them. But none of them laid on the visitor as any sort of obligation. And as we walk the trail, even if I don’t embrace the offered pause, the chance itself suggests thoughts and images as I pass that the silence enlarges. I sit on that bench even as I walk past; I cross the bridge inwardly, even if it spans a trail I don’t take.

Sometimes a sign presents choices worthy of Yogi Berra’s “When you come to a fork in the road, take it.”

Perhaps it’s fitting to close with the North, direction of earth, stone, embodiment, manifestation — all qualities matching the interfaith vision of this place.

/|\ /|\ /|\
This is the 200th post at A Druid Way. Thanks, everyone, for reading!
[Related posts: Shinto & Shrine Druidry 1 | 2 | 3 || Shinto — Way of the Gods || Renewing the Shrine 1 | 2 || My Shinto 1 | 2 ]

The continuing interest among visitors here at A Druid Way in the posts on Shinto says hunger for the Wild, for spiritual connection to wilderness and its rejuvenating spirit, and potentially for Shrine Druidry, remains unabated. No surprise — in our hunger we’ll turn almost anywhere. What forms our response to such hunger may take is up to us and our spiritual descendants. Spirit, the goddesses and gods, the kami, the Collective Unconscious, Those Who Watch, your preferred designation here _____, just might have something to say about it as well.
What we know right now is that we long for spirit, however we forget or deny it, papering it over with things, with addictions and with despair in this time of many large challenges — a hunger more alive and insistent than ever. And this is a good thing, a vital and necessary one. In an artificial world that seems increasingly to consist of hyped hollowness, we stalk and thirst for the real, for the healing energies the natural world provides all humans as a birthright, as participants in its “spiritual economy” of birth, growth, death and rebirth.
As physical beings we live in a world where breathing itself can be a spiritual practice, where our heartbeats sound out rhythms we are born into, yet often and strangely have tried to flee. Even this, my sadness and loss, can be prayer, if I listen and let them reach and teach me, if I walk with them toward something larger, yet native to blood and bone, leaf and seed, sun and moon and stars. Druidry, of course, is simply one way among many to begin.
/|\ /|\ /|\
If you know Kipling‘s Just So stories, you’re familiar with “The Cat That Walked By Himself.” The cat in question consistently asserts, “All places are alike to me.” But for people that’s usually NOT true. Places differ in ease of access, interest, health, natural beauty, atmosphere — or, in convenient shorthand, spirit. Shrines acknowledge this, even or especially if the shrine is simply a place identified as Place, without any sacred buildings like Shinto has — a place celebrated, honored, visited as a destination of pilgrimage, as a refuge from the profane, as a portal of inspiration.
Here’s a local (to me) example of a place in Vermont I’ll be visiting soon and reporting on, one that sounds like an excellent direction for a Shrine Druidry of the kind people are already starting to imagine and create. It’s called Spirit in Nature, and it’s a multi-faith series of meditation trails with meditation prompts. Its mission statement gets to the heart of the matter:
Spirit in Nature is a place of interconnecting paths where people of diverse spiritual traditions may walk, worship, meet, meditate, and promote education and action toward better stewardship of this sacred Earth.
Spirit in Nature is a non-profit, 501 (c)3 tax-exempt organization, always seeking new members, local volunteers to build and maintain paths, financial contributions, and interest from groups who would like to start a path center in their own area.
/|\ /|\ /|\
So much lies within the possible scope of Shrine Druidry it’s hard to know where to start. Many such sites (and more potential sites) already exist in various forms. Across Europe, and to a lesser degree in North America (public sites, that is: private Native American and Pagan sites exist in surprising numbers), are numerous sacred-historical sites (some of which I’ll examine in a coming post), often focusing around a well, cave, tree, waterfall, stone circle, garden, grove, etc. Already these are places of pilgrimage for many reasons: they serve as the loci of national and cultural heritage and historical research, as commemorative sites, spiritual landmarks, orientations in space and time, as treasures of ethnic identity — the list goes on. Quite simply, we need such places.

Lower Falls, Letchworth St. Pk, NY. Image by Wikipedia/Suandsoe.
The national park system of the U.S., touted as “America’s Best Idea” (also the title of filmmaker Ken Burns’ series), was established to preserve many such places, though without any explicit markers pointing to spiritual practice. But then of course we already instinctively go to parks for healing and restoration, only under the guise of “vacations” and “recreation.” And many state parks in the U.S. extend the national park goal of preserving public access to comparatively unspoiled natural refuges. Growing up, I lived a twenty-minute bike ride from Letchworth State Park in western NY: 14,000 acres of forest surrounding deep (in places, over 500 feet) gorges descending to the Genesee River. Its blessing follows me each time I remember it, or see an image of it, and in attitudes shaped there decades ago now. May we all know green cathedrals.
I’ll talk more about shrines on other scales, small and large, soon, and tackle more directly some of the similarities and differences between Shinto and Druidry. I’ll also look at some of the roles practitioners of earth-centered spiritualities can — and already do — play in connection to the creation and support of shrines.
/|\ /|\ /|\
Images: spider web; Lower Falls at Letchworth State Park, New York.
[Related posts: Shinto & Shrine Druidry 1 | 2 | 3 || Shinto — Way of the Gods || Renewing the Shrine 1 | 2 || My Shinto 1 | 2 ]
 I’ve mentioned Shinto and Tsubaki Grand Shrine before in these pages — a lovely shrine in Granite Falls, WA, about an hour north-northeast of Seattle. Recently during our car tour that included the Pacific Northwest, my wife and I “made omairi” or paid a visit on a sunny July day. The idiom “pay” is illuminating: some kinds of visits can be the fulfillment of a religious vow, a pilgrimage we dedicate to a spirit or an ideal — acts, in other words, performed at least potentially in fuller consciousness than usual. True, “the bow can’t always be bent,” as the old occult proverb goes; we “have to live in the real world,” as my mother used to admonish me. But you quickly find that cultivating regular times of intention and focus brings spiritual advantages just as it does other kinds of advantage in other aspects of life.
I’ve mentioned Shinto and Tsubaki Grand Shrine before in these pages — a lovely shrine in Granite Falls, WA, about an hour north-northeast of Seattle. Recently during our car tour that included the Pacific Northwest, my wife and I “made omairi” or paid a visit on a sunny July day. The idiom “pay” is illuminating: some kinds of visits can be the fulfillment of a religious vow, a pilgrimage we dedicate to a spirit or an ideal — acts, in other words, performed at least potentially in fuller consciousness than usual. True, “the bow can’t always be bent,” as the old occult proverb goes; we “have to live in the real world,” as my mother used to admonish me. But you quickly find that cultivating regular times of intention and focus brings spiritual advantages just as it does other kinds of advantage in other aspects of life.
 Tsubaki finds a working balance in explaining just enough about itself and about Shinto to the visitor who may know little about either. Shrines express unique and individual presences, and Tsubaki is no different. We can argue till the cows come home and make their own butter whether such distinctiveness comes from human intention solely, or from a happy cooperation of human and divine. What remains is the shrine itself, beyond mere debate: a place to visit, breathe, absorb, reflect on, and if you feel called to do so, revere and commune.
Tsubaki finds a working balance in explaining just enough about itself and about Shinto to the visitor who may know little about either. Shrines express unique and individual presences, and Tsubaki is no different. We can argue till the cows come home and make their own butter whether such distinctiveness comes from human intention solely, or from a happy cooperation of human and divine. What remains is the shrine itself, beyond mere debate: a place to visit, breathe, absorb, reflect on, and if you feel called to do so, revere and commune.
Tsubaki aids visitors in doing this. Here is the shrine’s temizuya, literally, “hand-water-place,” a feature at most shrines, offering an opportunity for ritual purification. The shrine offers a bilingual placard explaining the temizu ritual. Participating (or not) is left beautifully up to us, especially on a day like this was, with no one around but one silent shrine tender, sweeping and cleaning. But the temizuya does stand ready as one invitation among many to make our own discoveries through performing a small ritual action.
 Of course, a shrine need not always explain. Tsubaki, like so much of Shinto, also demonstrates the value of silence in fostering encounters with the natural world. They are not separate things; the human is part of the world of the kami, of spirit.
Of course, a shrine need not always explain. Tsubaki, like so much of Shinto, also demonstrates the value of silence in fostering encounters with the natural world. They are not separate things; the human is part of the world of the kami, of spirit.
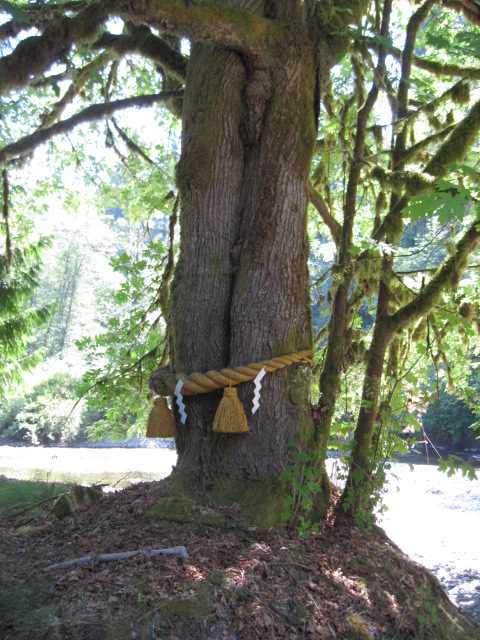

From another viewpoint, a shrine simply acknowledges what is already present, whether it chooses to point our attention to it, or bring us together by putting us in the same place. Here is the path from the central shrine down to the gravelly bed of the Pilchuck River. There you can see another small shrine (in the center of the picture, looking something like a tall sawhorse draped with white flags) standing near the water’s edge.


The plaque above adjoining the emaden explains another Shinto practice. Below is the emaden itself.

Less formal are the written prayers tied to natural features like trees and to man-made objects. And many Westerners have become familiar with Tibetan prayer flags. Odd that in the West a prayer is considered primarily a verbal action. The silent written prayer can stay in place; we can walk away, knowing our petition or vow or praise or thanks remain, where we made them. We wish for a change, a response, to manifest at least in part in this natural world. Then let our petition, our expression, our acknowledgement of spirit linger in the world, till the world’s elemental and spiritual forces reclaim them.

In addition to other kami, Tsubaki also enshrines America Kokudo Kunitama-no-Kami, the kami protector of the North American continent.
In the next post, I’ll look at some possibilities for what Shrine Druidry could look like as an expression of Druidic experience.
/|\ /|\ /|\
Updated 9 Oct 2015
You may know some of “them.” (What’s it say about us that we say “them”?) They’re often wonderful people, they raise families, they “contribute to society,” they’re fun to be around — and they may seem not to have a religious or spiritual bone in their bodies. And that’s not only something to “tolerate” or “accept.” It’s just as it should be. “I desire that there may be as many different persons in the world as possible; but I would have each one be very careful to find out and pursue his own way, and not his father’s or his mother’s or his neighbor’s instead,” says H. D. Thoreau.
Two couples whose company my wife and I delight in and seek out certainly qualify as non-religious: you can see their unease or discomfort if the topic happens to come up in conversation. An innocent question, or a comment in passing. “What’s that pin you’re wearing?” or “What did you do last month when you were in Minneapolis?” And hearing our answer, a kind of stiffness, a change in expression, a wilting, or wariness. “Oh no,” you can practically hear them thinking. “We’re going there again.”
And my wife and I laugh about it afterward. You get it, right? So often we’ve been the defensive ones, either avoiding the topic altogether, or passing off our beliefs with a quick, casual acknowledgment and then turning the talk in another direction, or (sigh) girding ourselves to explain, justify, account yet again for our non-mainstream practices and events and perspectives. The lesson for us continues to be this: if the opportunity opens up, find a way to talk about day-to-day benefits rather than beliefs, seek the common ground we all know from living on this planet, demonstrate it as a part of our lives, which they do care about. Then move on. Build trust, keep the lines of communication open, share your vulnerability and — as needed — shut up. You know: basic relationship stuff.
On our recent car trip, which I’ve touched on in the last several posts, we managed to reconnect with colleagues from over 25 years ago, a couple I worked with during my year of teaching in Changsha in the People’s Republic of China in the late 80s. We’d fallen out of touch: the first of their three children arrived, three of the four of us were back in school, several of us were patching together jobs out of already unconventional work histories, and both of our families moved at least a couple of times to accomplish these things.
 We joked about our reunion later, over a dinner of home-made jiaozi. Making and eating them had become a lovely family tradition for them after China. The four of us and their youngest daughter, now 19, stood around their dining room table, filling and wrapping and talking, brushing the jiaozi wrappers with the cornstarch-water mix to seal them, then watching as the plump crescent dumplings steamed. Earlier we’d met for lunch in a restaurant, in case any of us had become raving loonies in the interim, and a convenient escape was needed. Eight hours later, we all knew we had nothing to fear. And the best demonstration, in the moment, of spirituality in all of our lives? Friendship, hospitality, a shared meal, simple pleasure in each other’s company. A touch of nostalgia didn’t hurt either.
We joked about our reunion later, over a dinner of home-made jiaozi. Making and eating them had become a lovely family tradition for them after China. The four of us and their youngest daughter, now 19, stood around their dining room table, filling and wrapping and talking, brushing the jiaozi wrappers with the cornstarch-water mix to seal them, then watching as the plump crescent dumplings steamed. Earlier we’d met for lunch in a restaurant, in case any of us had become raving loonies in the interim, and a convenient escape was needed. Eight hours later, we all knew we had nothing to fear. And the best demonstration, in the moment, of spirituality in all of our lives? Friendship, hospitality, a shared meal, simple pleasure in each other’s company. A touch of nostalgia didn’t hurt either.
/|\ /|\ /|\
Image of jiaozi steaming: me. Actual kitchen, steamers, stove, etc., courtesy of S. T.
Edited: 2 Aug. 2014
 Suffice it to say that not one of the six living Celtic tongues is secure enough that its advocates can relax into anything resembling the ease of speakers of a world language like English. So why not learn one of these endangered languages (or revive Galatian)? After all, with such knowledge comes the ability to experience a living Celtic culture from the inside, as well as gain access in the original languages to texts that nourish Druid practice and thought. One more speaker is one more voice against linguistic and cultural extinction. In the title and first section above I invoke Brighid/Bríd and Ogma/Oghma, to give the ancient and modern Irish forms of their names. With the experiences of many contemporary and ancient polytheists in mind, I can say with some confidence that the gods honor those who go to the trouble to learn the old languages and speak to them using even a little of the ancestral tongues.
Suffice it to say that not one of the six living Celtic tongues is secure enough that its advocates can relax into anything resembling the ease of speakers of a world language like English. So why not learn one of these endangered languages (or revive Galatian)? After all, with such knowledge comes the ability to experience a living Celtic culture from the inside, as well as gain access in the original languages to texts that nourish Druid practice and thought. One more speaker is one more voice against linguistic and cultural extinction. In the title and first section above I invoke Brighid/Bríd and Ogma/Oghma, to give the ancient and modern Irish forms of their names. With the experiences of many contemporary and ancient polytheists in mind, I can say with some confidence that the gods honor those who go to the trouble to learn the old languages and speak to them using even a little of the ancestral tongues. One early question to answer in birthing a Celtic conlang is Q or P. No, that’s not some password you have to know in order to gain admission to the Secret Circle of All Druidry (SCOAD), or a riddle posed by the Planetary High Holy Archdruid. P- and Q-Celtic are shorthand for a linguistic division that usefully divides the six living Celtic tongues into two groups of three, based on their treatment of the Indo-European *kw- in words like *kwetwores “four,” Proto Celtic *kwetwar-, with Irish ceathair, Gaelic ceithir, Manx kaire for the Q-side, and Breton pevar, Cornish pesvar and Welsh pedwar for the P-side. Of course, being next-door neighbors as well as cousins, the six languages also borrowed from each other through their centuries together, which delightfully muddies the waters of linguistic post-gnostication (“knowing after the fact,” like pro-gnostication, only not). Flip a coin, go with your gut, follow your own esthetic, pray, do a divination, or some idiosyncratic combo all your own.
One early question to answer in birthing a Celtic conlang is Q or P. No, that’s not some password you have to know in order to gain admission to the Secret Circle of All Druidry (SCOAD), or a riddle posed by the Planetary High Holy Archdruid. P- and Q-Celtic are shorthand for a linguistic division that usefully divides the six living Celtic tongues into two groups of three, based on their treatment of the Indo-European *kw- in words like *kwetwores “four,” Proto Celtic *kwetwar-, with Irish ceathair, Gaelic ceithir, Manx kaire for the Q-side, and Breton pevar, Cornish pesvar and Welsh pedwar for the P-side. Of course, being next-door neighbors as well as cousins, the six languages also borrowed from each other through their centuries together, which delightfully muddies the waters of linguistic post-gnostication (“knowing after the fact,” like pro-gnostication, only not). Flip a coin, go with your gut, follow your own esthetic, pray, do a divination, or some idiosyncratic combo all your own.











































